2025年12月3日
Azure AI Searchの10万件を超えるドキュメントがあるインデックスを救いたい
この記事は、FUJITSU Advent Calendar 2025 3日目の記事です。昨日は @norikmb の Dependency Proxy と Renovate に関する記事 でした。ハマりポイントを記事にしておくことって有益ですよね。今日の記事もそんな感じです。
Azure AI Search ではクエリで一括取得できる上限が10万件までという仕様があります。そのためインデックス作成時にスキーマ検討をミスって、どのフィールドもソート可能(sortable)じゃない状況にしてしまうと、どうやっても10万件を超えた分のデータは取得できない……お引越しもできない……というトホホな状況になります。
今回はその状況に対処する方法を調べていたら(Azure が提供している)非公式のサンプルで解決策があったので試してみました。
環境
- Azure AI Search Free プラン
- Python 3.12.0

解決策の概要
Resumable backup and restore for very large indexes
- Sortable なフィールドとして、タイムスタンプのフィールドを追加で定義する
- タイムスタンプのフィールドの値が null な10万件を取得し、ランダムな値を入れる
- これを繰り返す
- タイムスタンプのフィールドでソートして10万件ずつ取得できるようになる
Sortable なフィールドないよ〜\(^o^)/って思ってましたが、ないなら作ればいいじゃん!ってことですね。かしこい。
やったこと
環境構築
uv init your-project-name uv add jupyterlab azure-search-documents==11.5.2 azure-identity python-dotenv aiohttp ipywidgets tqdm
JupyterLab を起動します。
jupyter lab
.env
AZURE_SEARCH_SOURCE_SERVICE_ENDPOINT=https://your-source-service.search.windows.net AZURE_SEARCH_DESTINATION_SERVICE_ENDPOINT=https://your-backup-service.search.windows.net AZURE_SEARCH_SOURCE_ADMIN_KEY=YOUR_ADMIN_KEY AZURE_SEARCH_INDEX=index-to-backup AZURE_SEARCH_TIMESTAMP_FIELD=timestampfilterfield
以下、Python コードは Jupyter 上でいい感じに実行してください。
from dotenv import load_dotenv from azure.identity.aio import DefaultAzureCredential from azure.core.credentials import AzureKeyCredential import os # Copy sample.env to .env and change the variables for your service load_dotenv(override=True) # The sample.env contains variables than what's needed for this code. Ignore any variables not used here. # Provide a search service containing the source index for the backup operation source_endpoint = os.environ["AZURE_SEARCH_SOURCE_SERVICE_ENDPOINT"] # Provide an admin API key if you're using key-based authentication. Using a key is optional. See https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/search/keyless-connections source_credential = AzureKeyCredential(os.getenv("AZURE_SEARCH_SOURCE_ADMIN_KEY")) if os.getenv("AZURE_SEARCH_SOURCE_ADMIN_KEY") else DefaultAzureCredential() # Provide a second search service as the destination for the new restored index destination_endpoint = os.environ["AZURE_SEARCH_DESTINATION_SERVICE_ENDPOINT"] destination_credential = AzureKeyCredential(os.getenv("AZURE_SEARCH_DESTINATION_ADMIN_KEY")) if os.getenv("AZURE_SEARCH_DESTINATION_ADMIN_KEY") else DefaultAzureCredential() # Name of the index to be backed up index_name = os.getenv("AZURE_SEARCH_INDEX", "") # Optionally, multiple indexes can be specified as a comma-separated list. If not specified, the value of AZURE_SEARCH_INDEX is used. index_names = os.getenv("AZURE_SEARCH_INDEXES", index_name).split(",") if "AZURE_SEARCH_INDEXES" in os.environ else [index_name] # Name of the timestamp field timestamp_field_name = os.environ["AZURE_SEARCH_TIMESTAMP_FIELD"]
10万件を超えるデータを投入
200,001件のデータを投入します。
from azure.search.documents.indexes.aio import SearchIndexClient from azure.search.documents.aio import SearchClient from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import SearchIndex, SimpleField, SearchableField, SearchFieldDataType from uuid import uuid4 count = 200_001 batch_size = 32000 docs_list_flat = [{"id": str(uuid4()), "content": "test"} for i in range(count)] docs_list = [docs_list_flat[i : i + batch_size] for i in range(0, count, batch_size)] async with SearchIndexClient(endpoint=source_endpoint, credential=source_credential) as source_index_client, SearchClient(endpoint=source_endpoint, credential=source_credential, index_name=index_name) as source_client: new_index = SearchIndex(name=index_name, fields=[ SimpleField(name="id", type=SearchFieldDataType.String, key=True, filterable=True), SearchableField(name="content", type=SearchFieldDataType.String), ]) await source_index_client.create_or_update_index(new_index) for docs in docs_list: result = await source_client.upload_documents(documents=docs)
タイムスタンプフィールドを追加
Resumable backup and restore for very large indexes の中のコードをそのまま実行します。
実行したコード
from azure.search.documents.indexes.aio import SearchIndexClient from azure.search.documents.aio import SearchClient from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import BinaryQuantizationCompression, SearchField from datetime import datetime, timedelta from uuid import uuid4 import random enable_compression = False # Copies an index definition from the source service to the destination async def copy_index_definition(source_index_client: SearchIndexClient, destination_index_client: SearchIndexClient, index_name: str): index = await source_index_client.get_index(index_name) # Check for any synonym maps synonym_map_names = [] for field in index.fields: if field.synonym_map_names: synonym_map_names.extend(field.synonym_map_names) # Copy over synonym maps if they exist for synonym_map_name in synonym_map_names: synonym_map = await source_index_client.get_synonym_map(synonym_map_name) await destination_index_client.create_or_update_synonym_map(synonym_map) if enable_compression: for profile in index.vector_search.profiles: if not profile.compression_name: profile.compression_name = "mycompression" index.vector_search.compressions.append( BinaryQuantizationCompression( compression_name="mycompression", rerank_with_original_vectors=True, default_oversampling=10 )) # Copy over the index await destination_index_client.create_or_update_index(index) # Method to convert a timestamp to datetime def datetime_to_timestamp(date: datetime) -> str: # Trim microseconds to milliseconds. Timestamp precision is to milliseconds only. See https://learn.microsoft.com/rest/api/searchservice/supported-data-types#edm-data-types-for-nonvector-fields for more information return date.strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%fZ")[:-3] + "Z" def get_random_timestamp(start_time: datetime, end_time: datetime) -> str: delta = end_time - start_time random_seconds = random.randint(0, int(delta.total_seconds())) return datetime_to_timestamp(start_time + timedelta(seconds=random_seconds)) # Add a timestamp field to the index async def add_timestamp_to_index(source_index_client: SearchIndexClient, source_client: SearchClient, index_name: str, timestamp_field_name: str, start_timestamp: datetime, end_timestamp: datetime): index = await source_index_client.get_index(index_name) timestamp_field_added = False key_field = None for field in index.fields: if not key_field and field.key: key_field = field if field.name == timestamp_field_name: timestamp_field_added = True if not timestamp_field_added: index.fields.append(SearchField(name=timestamp_field_name, type="Edm.DateTimeOffset", facetable=False, filterable=True, sortable=True, hidden=False)) await source_index_client.create_or_update_index(index) # Create a session when paging through results to ensure consistency in multi-replica services # For more information, please see https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/search/index-similarity-and-scoring#scoring-statistics-and-sticky-sessions session_id = str(uuid4()) get_next_results = True while get_next_results: total_results_size = 0 filter = f"{timestamp_field_name} eq null" results = await source_client.search( search_text="*", top=100000, filter=filter, session_id=session_id, select=[key_field.name] ) results_by_page = results.by_page() async for page in results_by_page: # Add a timestamp to this page of results update_page = [{ key_field.name: item[key_field.name], timestamp_field_name: get_random_timestamp(start_timestamp, end_timestamp) } async for item in page] if len(update_page) > 0: await source_client.merge_documents(update_page) total_results_size += len(update_page) # If any results were returned, it's possible there's more documents without a timestamp # Continue the search get_next_results = total_results_size > 0
(Optional) Add a timestamp column
If you don't have a timestamp column to use for resuming, you can add one by generating new timestamps. It's important to attempt to evenly distribute these timestamps across your index
from datetime import datetime, time for index_name in index_names: async with SearchIndexClient(endpoint=source_endpoint, credential=source_credential) as source_index_client, SearchClient(endpoint=source_endpoint, credential=source_credential, index_name=index_name) as source_client: now = datetime.now() start_of_day = datetime.combine(now.date(), time.min) end_of_day = datetime.combine(now.date(), time.max) await add_timestamp_to_index(source_index_client, source_client, index_name, timestamp_field_name, start_timestamp=start_of_day, end_timestamp=end_of_day)
完了すると、Sortable/Filterable なフィールドが追加されています。
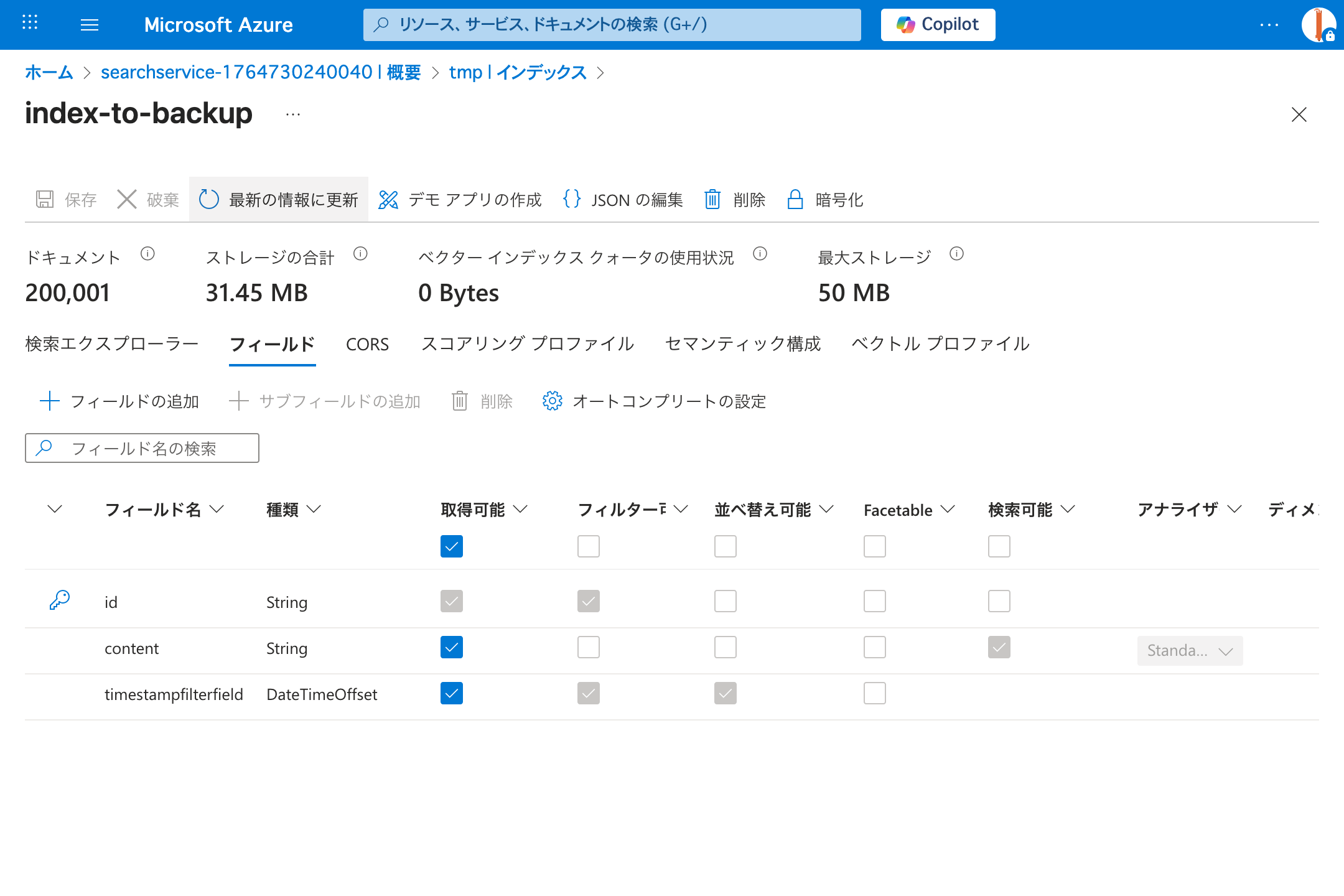
全件取得してみる
バックアップ&リストアすると無料枠の50MBを超えてしまうので、取得できるかだけ試してみます。 配布されている Notebook の一部を切り出して実行します。
from typing import AsyncGenerator, Optional from azure.search.documents.indexes.aio import SearchIndexClient from azure.search.documents.aio import SearchClient from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import SearchIndex, SimpleField, SearchableField, SearchFieldDataType from uuid import uuid4 # Resume fetching search results from a source index for backup. # May have timestamp bounds if resuming from a previous backup job or using parallel backup jobs async def resume_backup_results(client: SearchClient, timestamp_field_name: str, timestamp: Optional[str], select=None) -> AsyncGenerator[list[dict], None]: # Create a session when paging through results to ensure consistency in multi-replica services # For more information, please see https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/search/index-similarity-and-scoring#scoring-statistics-and-sticky-sessions session_id = str(uuid4()) # The maximum number of results from a single search query is 100,000. This can be exceeded by using sorting and filtering # For more information, please see https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/search/search-pagination-page-layout#paging-through-a-large-number-of-results max_results_size = 100000 get_next_results = True while get_next_results: total_results_size = 0 filter = None if timestamp: # If using a single timestamp, find all records greater or equal than it filter = f"{timestamp_field_name} ge {timestamp}" results = await client.search( search_text="*", order_by=f"{timestamp_field_name} asc", top=max_results_size, filter=filter, session_id=session_id, select=select ) results_by_page = results.by_page() async for page in results_by_page: next_page = [item async for item in page] # Count how many results are returned total_results_size += len(next_page) if len(next_page) == 0: break yield next_page timestamp = next_page[-1][timestamp_field_name] # If the maximum amount of results were returned, it's possible there's more results after the last timestamp searched # Continue the search using the most recent timestamp get_next_results = total_results_size == max_results_size async with SearchClient(endpoint=source_endpoint, credential=source_credential, index_name=index_name) as source_client: results = [item async for page in resume_backup_results(source_client, timestamp_field_name, None) for item in page] print(len(results))
結果は 200004 となりました。
投入したデータの件数より多いですが、フィルタを f"{timestamp_field_name} gt {timestamp}" に変えたら 199998 になってしまったので、timestamp の境界上の値が複数あるのだと思われます。
取得できないのはどうしようもないですが、重複して取得されている分にはアプリ側の作りでカバーできるかと思うので、頑張りましょう。この記事が10万件上限に絶望している方に届けば幸いです。☺️
